Acumatica Localization for Vietnam: What You Need To Know For Success
Acumatica Localization for Vietnam is essential for businesses looking to comply with Vietnam Accounting Standards (VAS) while leveraging the power of cloud ERP. This article explores key localization requirements, gaps in standard Acumatica functionality, and best practices for achieving financial compliance.
Understanding Vietnam Accounting Standards (VAS)
Vietnamese Accounting Standards (VAS) are issued by the Ministry of Finance (MoF) in Vietnam, governing financial reporting for businesses operating in the country. Key characteristics of VAS include:
- Strict regulatory compliance: Requires detailed financial reports following Circular 200 (TT200) and Circular 133.
- Limited flexibility: Unlike IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards), VAS allows minimal adjustments.
- Emphasis on statutory reporting: Companies must submit statutory financial reports, including Balance Sheets, Profit & Loss Statements, and VAT declarations.
Key Differences Between VAS and IFRS
While VAS is based on IFRS principles, it has several localized modifications to align with Vietnamese tax regulations and reporting structures. Key differences include:
| Criteria | IFRS | VAS |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Statements | 5 components: Balance Sheet, P&L, Cash Flow, Changes in Equity, Notes | 4 components: Balance Sheet, P&L, Cash Flow, Notes (No Statement of Changes in Equity) |
| Chart of Accounts (COA) | No mandatory COA | Standard COA required under Circular 200/133 |
| Reporting Currency | Any functional currency | Default is VND, foreign currency must be converted for reporting |
| Fixed Asset Recognition | No value threshold | Minimum VND 30 million, otherwise classified as prepaid expenses |
| Fair Value Measurement | Allowed | Only historical cost model permitted |
| Revenue Recognition | Follows IFRS 15 five-step model | Modified IAS 18 approach, no direct IFRS 15 compliance |
| Corporate Income Tax (CIT) | Requires deferred tax accounting | Deferred tax not required |
Key Requirements for Acumatica Localization for Vietnam
For Acumatica to be fully compliant with Vietnamese regulations, it must support localized financial reporting, tax compliance, and government-mandated templates. Essential components of an Acumatica localization package include:
1. Customized Chart of Accounts (COA)
- Pre-configured COA aligned with VAS requirements under Circular 200 & 133.
- Ability to map international reporting to local statutory formats.
2. Tax Localization (VAT, CIT, PIT)
- Automatic VAT calculation based on Vietnam’s tax structure.
- Pre-built VAT reports formatted according to government templates.
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT) computation, with compliance to local tax rules.
- Personal Income Tax (PIT) module for payroll tax compliance.
3. Statutory Financial Reports
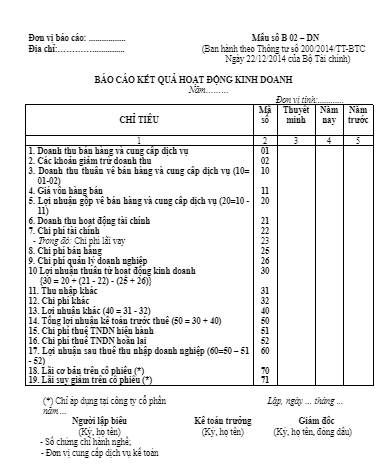
Acumatica Localization for Vietnam must generate the following statutory reports automatically:
- Balance Sheet (Bảng Cân Đối Kế Toán)
- Income Statement (Báo Cáo Kết Quả Hoạt Động Kinh Doanh)
- Cash Flow Statement (Báo Cáo Lưu Chuyển Tiền Tệ)
- Trial Balance (Bảng Cân Đối Phát Sinh)
- General Ledger (Sổ Cái Tổng Hợp)
- VAT Purchase & Sales Reports (Bảng Kê Hóa Đơn GTGT)
- Fixed Asset Depreciation Reports (Sổ Chi Tiết Tài Sản Cố Định)
4. E-Invoice & Tax Declaration Compliance
Vietnam mandates electronic invoicing (e-Invoice) and e-Tax reporting to the General Department of Taxation (GDT). Acumatica’s localization module should include:
- Integration with Vietnam’s e-Invoice providers (e.g., MISA, FPT.eInvoice).
- Automated invoice issuance per GDT regulations.
- Electronic tax submission for VAT and CIT.
Approaches to Implementing Acumatica Localization for Vietnam
Businesses implementing Acumatica in Vietnam can choose one of the following approaches:
Approach A: Using Acumatica Report Builder
✅ Advantages:
- Flexible & user-friendly: Allows customization of reports.
- Drill-down capabilities: Enables easy access to detailed transactions.
- Supports both statutory & management reporting.
❌ Disadvantages:
- Format limitations: Reports may require manual adjustments.
- Post-processing in Excel is often necessary before submission.
Approach B: Using Suitelet-Based Custom Reports
✅ Advantages:
- Exact compliance with TT200 templates.
- Ready-to-submit reports without additional formatting.
❌ Disadvantages:
- Less flexible for customization.
- Limited drill-down functionality compared to Acumatica’s native reports.
Key Factors for Successful Acumatica Localization for Vietnam
To successfully implement Acumatica Localization for Vietnam, businesses must consider:
1. Expert Consultation
Engage Acumatica partners who have deep expertise in Vietnamese accounting regulations and local tax laws.
2. Bilingual Accounting Support
Ensure that consultants and accounting teams are fluent in both English and Vietnamese to facilitate COA mapping and regulatory compliance.
3. Automation & Compliance
Automate e-Invoice generation, tax calculations, and statutory reporting to reduce compliance risks and manual errors.
4. Cloud-Based Financial Management
Acumatica’s true cloud ERP enables real-time financial reporting, audit trails, and government compliance.
Conclusion: Achieve Compliance and Efficiency with Acumatica Localization for Vietnam
Implementing Acumatica Localization for Vietnam is crucial for businesses that want to stay compliant with Vietnam Accounting Standards (VAS) while leveraging the benefits of a modern cloud ERP. By integrating automated statutory reporting, tax localization, e-invoicing, and multi-book accounting, Acumatica enables companies to streamline financial management, reduce compliance risks, and improve operational efficiency.
With S4 Consulting’s Acumatica Localization Services, businesses in Vietnam can confidently navigate local regulatory requirements, optimize financial reporting, and drive growth through data-driven decision-making. Whether you’re transitioning from legacy systems or looking to enhance your current ERP capabilities, Acumatica provides the scalability and flexibility needed to support your expansion.